Energy - DNE21+: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Text replacement - "(Image:.*IMPORT\/attachments\/[0-9]*\/[0-9]*.png\|)" to "File:") |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
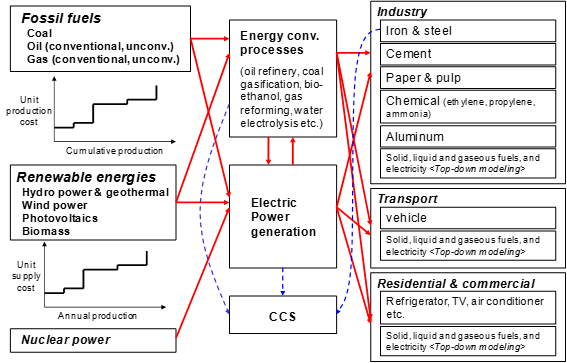
It includes eight types of primary energy sources; coal, oil (conventional and unconventional), natural gas (conventional and unconventional), hydro power and geothermal, nuclear, wind power, photovoltaics and biomass). Interregional transportation of energy (coal, oil natural gas, synthetic oil, ethanol, electrical power and hydrogen) and CO2 are incorporated in the model. As technological options, various types of energy-conversion technologies are explicitly modeled, such as electricity generation, oil refinery, natural gas liquefaction, coal gasification, and water electrolysis, methanol synthesis. The end-use sector are disaggregated into four types of secondary energy carriers: 1) solid fuel, 2) liquid fuel, 3) gaseous fuel, and 4) electricity. The demands for these energy carriers are endogenously calculated in a top-down fashion using long-term price elasticities in other cases than the reference case. | It includes eight types of primary energy sources; coal, oil (conventional and unconventional), natural gas (conventional and unconventional), hydro power and geothermal, nuclear, wind power, photovoltaics and biomass). Interregional transportation of energy (coal, oil natural gas, synthetic oil, ethanol, electrical power and hydrogen) and CO2 are incorporated in the model. As technological options, various types of energy-conversion technologies are explicitly modeled, such as electricity generation, oil refinery, natural gas liquefaction, coal gasification, and water electrolysis, methanol synthesis. The end-use sector are disaggregated into four types of secondary energy carriers: 1) solid fuel, 2) liquid fuel, 3) gaseous fuel, and 4) electricity. The demands for these energy carriers are endogenously calculated in a top-down fashion using long-term price elasticities in other cases than the reference case. | ||
[[ | [[File:55902773.png]] | ||
Figure 6 Outline of energy flows in DNE21+ | Figure 6 Outline of energy flows in DNE21+ | ||
Latest revision as of 12:51, 24 August 2016
| Corresponding documentation | |
|---|---|
| Previous versions | |
| Model information | |
| Model link | |
| Institution | Research Institute of Innovative Technology for the Earth (RITE), Japan, http://www.rite.or.jp/en/. |
| Solution concept | |
| Solution method | |
| Anticipation | |
DNE21+ includes a detailed description of energy carriers and conversion technologies.
It includes eight types of primary energy sources; coal, oil (conventional and unconventional), natural gas (conventional and unconventional), hydro power and geothermal, nuclear, wind power, photovoltaics and biomass). Interregional transportation of energy (coal, oil natural gas, synthetic oil, ethanol, electrical power and hydrogen) and CO2 are incorporated in the model. As technological options, various types of energy-conversion technologies are explicitly modeled, such as electricity generation, oil refinery, natural gas liquefaction, coal gasification, and water electrolysis, methanol synthesis. The end-use sector are disaggregated into four types of secondary energy carriers: 1) solid fuel, 2) liquid fuel, 3) gaseous fuel, and 4) electricity. The demands for these energy carriers are endogenously calculated in a top-down fashion using long-term price elasticities in other cases than the reference case.
Figure 6 Outline of energy flows in DNE21+